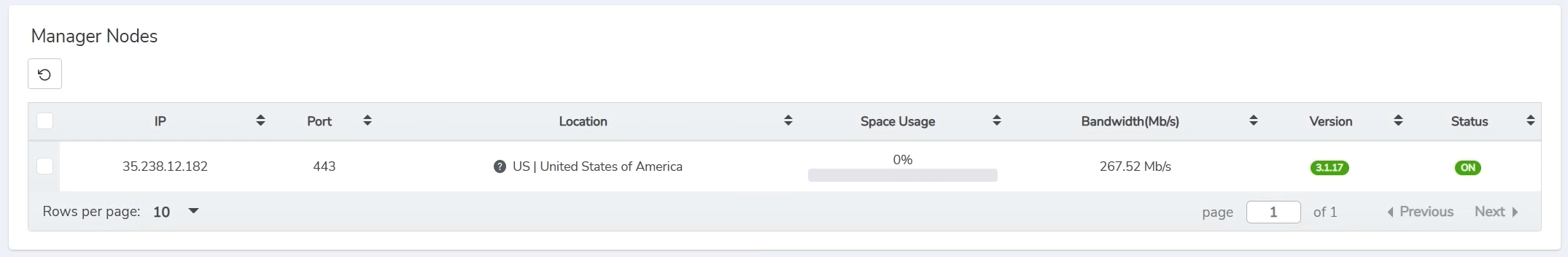
Run Meson ARM Node 101
Deploy Requirements
- A Public(Static/Dynamic) IP or A DHCP Reservation
- An ARM-based Devices(Raspberry Pi/Soft Router/Jetson Nano etc.)
- Opening the port of the firewall (default: 443, support for custom server ports)
- Providing enough Storage (default minimum requirements: 20G)
Supported Unix/Linux operating systems
| OS | Website |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm |
| Debian | https://www.debian.org/ports/arm |
| Raspberry Pi OS | https://www.raspberrypi.com/software |
| Fedora | https://arm.fedoraproject.org |
| OpenWrt | https://openwrt.org |
| Armbian | https://www.armbian.com |
| DietPi | https://dietpi.com |
| Manjaro | https://manjaro.org/download/#ARM |
| Arch Linux | https://archlinuxarm.org |
| openSUSE | https://get.opensuse.org |
| Asahi Linux | https://asahilinux.org |
Register
https://dashboard.meson.network/register
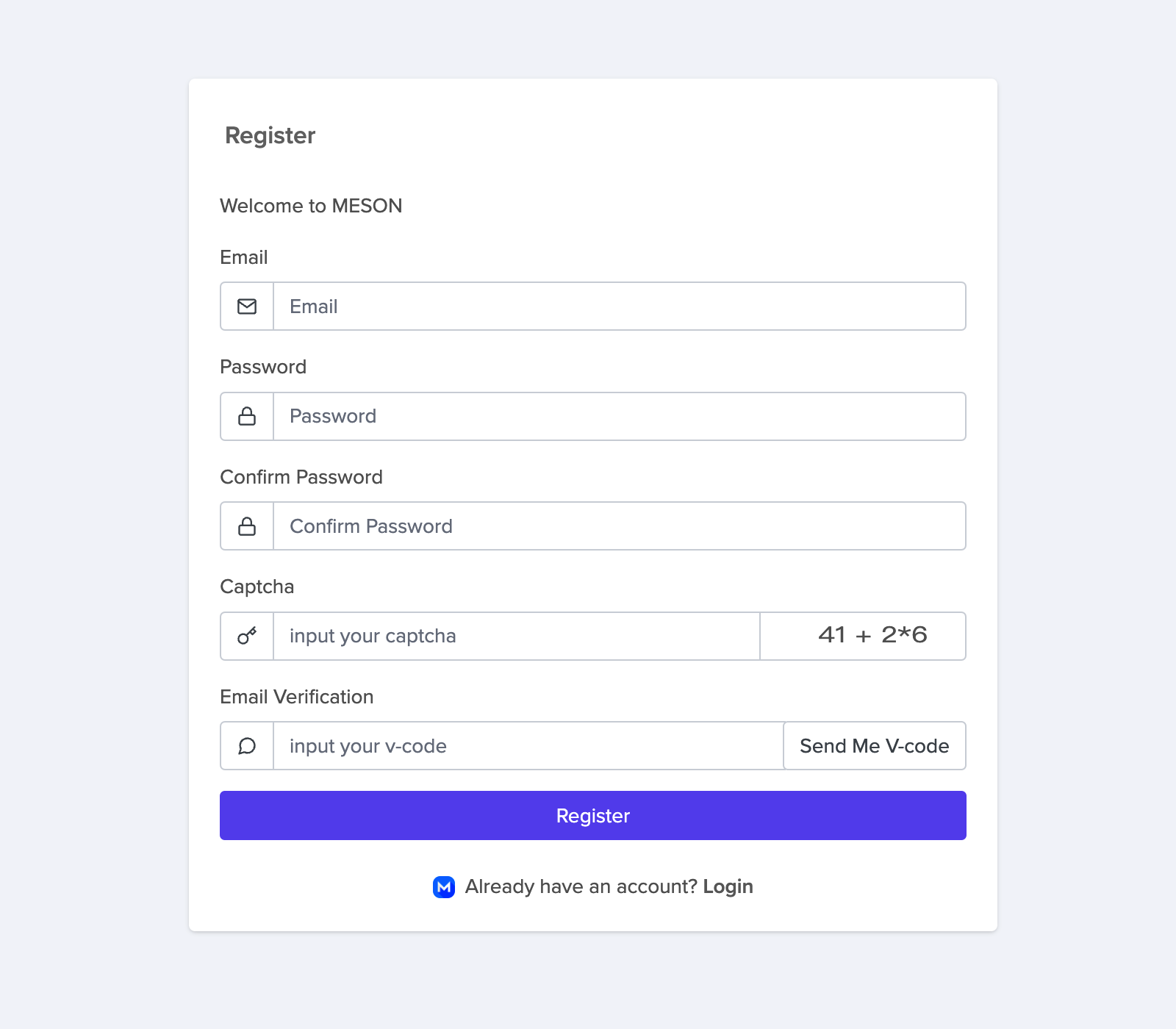
Click the button “Nodes” and you can find out your token and installation tutorial in this page
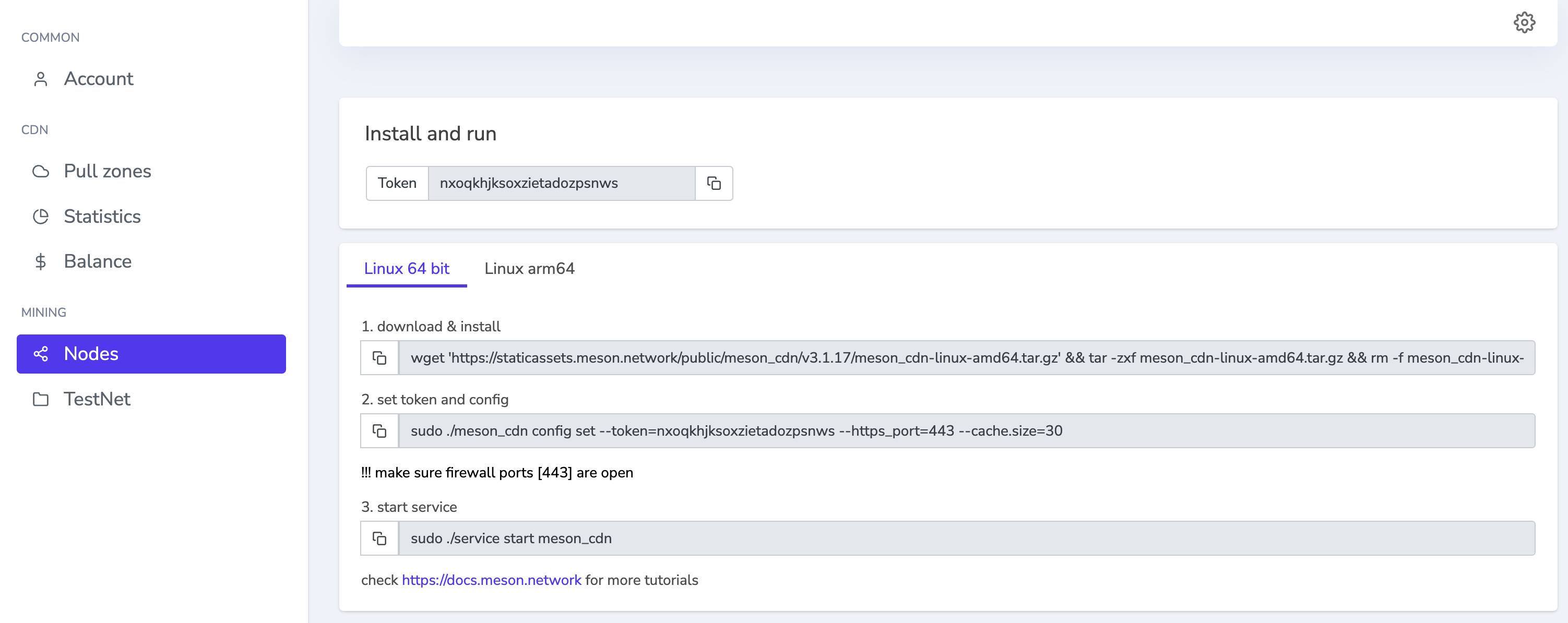
How to Install Meson on ARM (Linux)?
1.Download & Install
wget 'https://staticassets.meson.network/public/meson_cdn/v3.1.18/meson_cdn-linux-arm64.tar.gz' && tar -zxf meson_cdn-linux-arm64.tar.gz && rm -f meson_cdn-linux-arm64.tar.gz && cd ./meson_cdn-linux-arm64 && sudo ./service install meson_cdn
wget 'https://github.com/daqnext/meson-terminal/releases/download/v3.1.18/meson_cdn-linux-arm.tar.gz' && tar -zxf meson_cdn-linux-arm.tar.gz && rm -f meson_cdn-linux-arm.tar.gz && cd ./meson_cdn-linux-arm && sudo ./service install meson_cdn
Check the output of uname -m. If the result is aarch32 you are running the ARM Linux kernel in 32-bit and if the result is aarch64 or arm64 you are running the kernel in 64-bit mode. check out List of ARM processors.
2.Set token and config
sudo ./meson_cdn config set --token=your token --https_port=443 --cache.size=30
When your ISP does not provide Static IP, you can need to set other ports other than 443.Valid values range from 1 through 65535.
In the example, I changed the default port to 1943.
sudo ./meson_cdn config set --token=your token --https_port=1943 --cache.size=30
Param List:
-token=your token # you can find out your token in nodes page
-https_port=443 # default is 443, support for custom server ports
-cache.size=30 # minimum: 20G, default: 30G
-cache.folder=xxxx # string, cache folder path, could be an absolute path
3.Start Service
sudo ./service start meson_cdn
How to Forward Ports on Your Router?
Learn to set up port forwarding, check out https://portforward.com or your Router's instructions.
Take Cisco DPC3941T XFINITY router for example, the basic process to port forwarding is:
1.Login to your Cisco DPC3941T XFINITY router.
- The default IP Address is:
10.0.0.1 - The default Username is:
admin - The default Password is:
password
2.Navigate to the port forwarding section.
Now we need to find the port forwarding section in your router. Here's how you do it. Starting from the first page in your router:
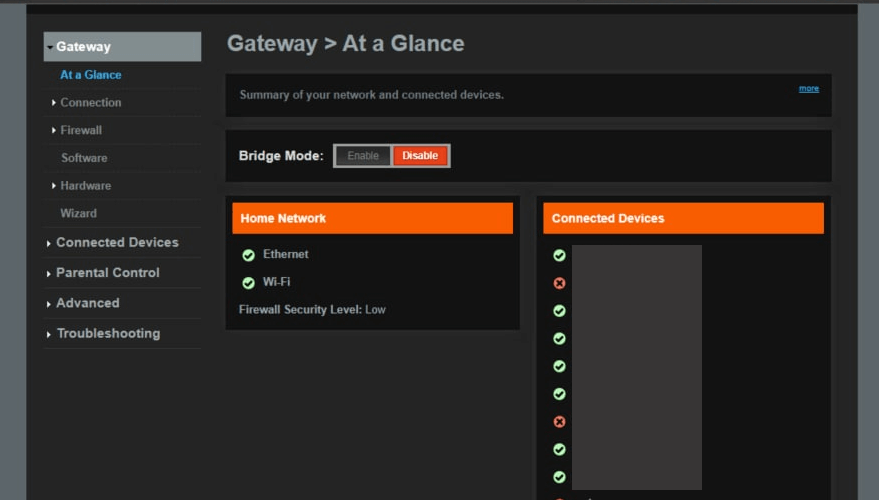
Click the Advanced link near the left of the page.
You should now see a new menu. In this new menu, click Port Forwarding.
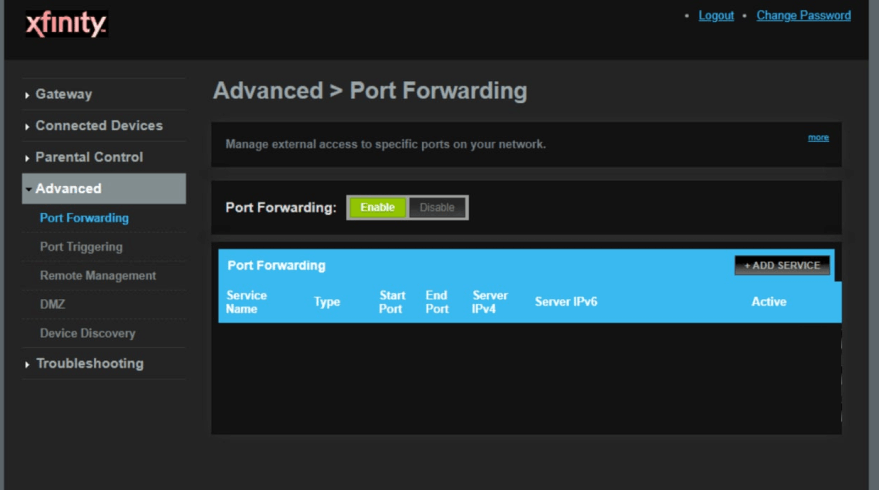
Click the Add Service button near the center of the page.
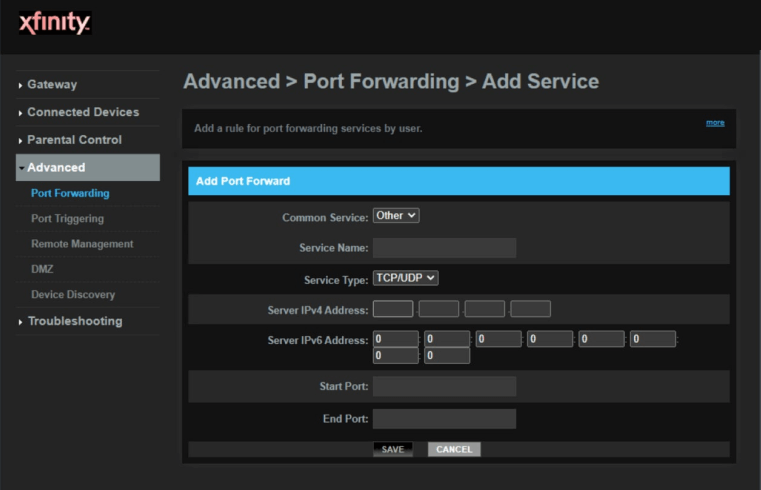
3.Create a port forward entry.
Select Other from the Common Service dropdown box.
Put a name for this forward in the Service Name box so that you can remember why you set this forward up.
Use the Service Type dropdown box to select the protocol type of the ports you are forwarding.
Enter the IP address that you are forwarding ports to in the Server IP Address box.
If you are forwarding a single port, enter that port number into the Start Port and the End Port boxes.
In the example, I changed the default port to 1943.
- TCP Ports:
1943 - UDP Ports:
1943
When you are done click the Save button.
Your ports should now be open. test if your ports are open.
After 2-3 minutes, you will have a new terminal record at terminals open in new node .